Stator machining solution ready for series production
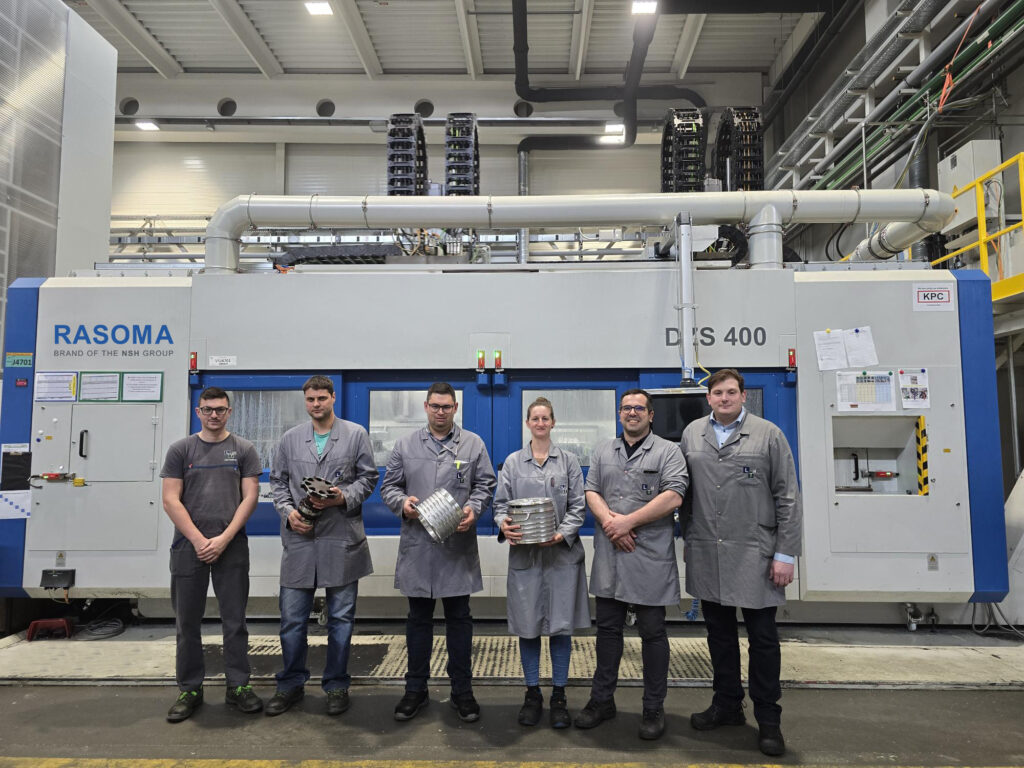
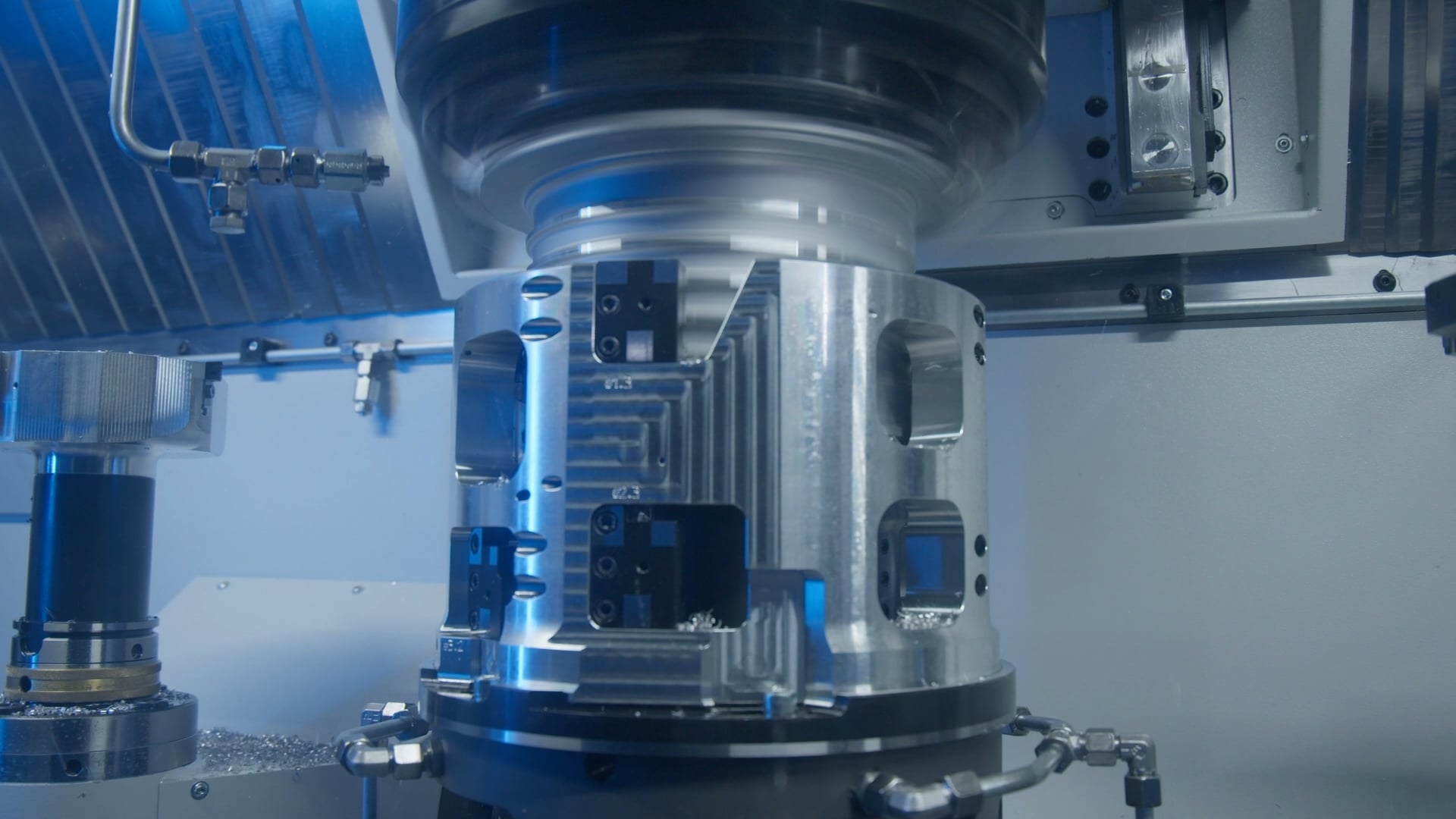

A process for complete machining of stator housings for electric motors, developed by Chemnitz machinery manufacturer NILES-SIMMONS and tool manufacturer MAPAL, has reached series production. Suppliers and OEMs now use it to produce components for drives in battery-powered electric vehicles and hybrid models.
Both manufacturers recently proved in a development project that highly cost-efficient and precise production of stator housings is possible on a pick-up lathe. The parts feature external ribs for cooling circuits and are installed in the larger motor housing.
Whilst NILES-SIMMONS used a converted modular lathe during development, a machine specifically designed for stator production has now entered the market. The basis for development was the vertical machining centre from the RASOMA brand, which, like NILES-SIMMONS, is an NSH Group brand. The RASOMA DZS 400-2 indicates operation with two workpiece spindles.
For series production, the machine features side-mounted pickup and drop-down areas for finished parts. Components are supplied and removed via conveyor belts. With manual assembly, 10 to 20 components can be buffered through automation, allowing multiple systems to operate simultaneously while workers attend to other processes. “We’ve realised highly simple automation as standard. No robots or blocks on the machine are required.Operators can place parts directly on the pallet belt,” explains Thomas Lötzsch, Sales Manager at NSH TECHNOLOGY.
The machine integrates easily into existing production environments, with compact installation dimensions of 7.50 by 2.60m. The RASOMA DZS 400-2 design was developed in collaboration with LTH Castings, a partner with extensive casting experience and expertise in machining complex, high-quality, thin-walled pressure die-cast aluminium components. The design, therefore, directly incorporates practical experience and user requirements.
Complete machining in two clamping systems
Finishing occurs on the vertical machine in two clamping systems. A clamping device picks up the workpiece from above and moves it to various machining stations. At a re-clamping station, the part is rotated 180 degrees and picked up by the second workpiece spindle for finishing. During second clamping, machining of the next component begins simultaneously at the first pick-up.
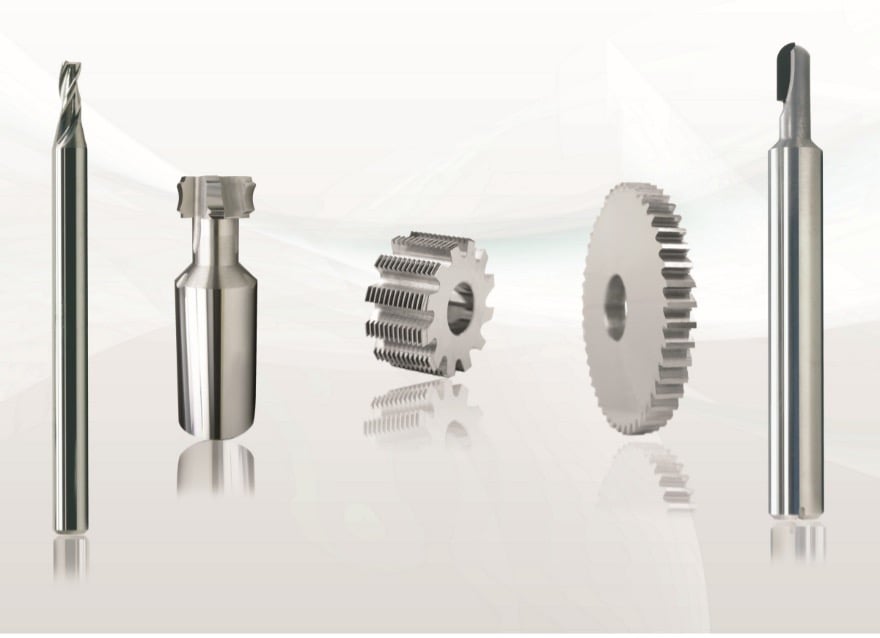
The process begins with pre-roughing the component’s various inner diameters. The tool remains stationary whilst the workpiece rotates. “Unlike conventional turning with a blade, machining with a four-blade ISO boring tool on an HSK-A 100 spindle takes just a quarter of the productive time,” says MAPAL regional sales manager André Ranke.
The inner tool also rotates. Tool speed and workpiece speed differences produce cutting speed at the inner blades. The bell-shaped outer tool remains stationary. The component is placed in the gap between inner and outer tools for machining. This patented process reduces forces on the clamping system, avoiding the need for complex workpiece clamping devices with vibration-damping for precise machining of thin-walled components. “When designing the tool, particular attention was paid to the large chip volume and significant forces generated, as simultaneous inner and outer diameter machining is unusual,” explains Michael Kucher, Component Manager E-Mobility at MAPAL.
During finishing, only the fine boring tool is driven whilst the component remains stationary. This prevents non-rotationally symmetrical workpiece shapes from causing material imbalances with negative impacts. The workpiece is then re-clamped and the outer area previously clamped in the flange area is machined. The re-clamping station can also relax the material before fine boring. The machine has two tool revolvers for driven tools carrying out further machining based on component requirements.
Faster and more stable than expected
“The RASOMA DZS 400-2 combines turning speed for pre-machining inner and outer contours with fine boring accuracy for finishing inner contours,” says Daniel Pilz, Project Leader at NSH TECHNOLOGY. With machine, tool technology, and process serialisation, positive prototype results were improved further. Process reliability exceeded expectations, allowing the targeted cutting speed of 700 m/min to be increased. “For aluminium machining, NILES-SIMMONS’ experience positively impacts tool technology and machine reliability,” explains Michael Kucher.
The RASOMA DZS 400-2 achieves much shorter chip-to-chip time than milling centres because all tools are already in the working area. This reduces non-productive time. Using this technology, studies anticipated 50% cycle time reduction.
Parts were initially measured, current guidance recommends testing one part per shift. Daniel Pilz uses figures to demonstrate this is more than adequate: “The RASOMA DZS 400-2 with special MAPAL tools achieves a process capability index over 1.67 for critical characteristics such as cylinder shape, diameter, and concentricity, meeting industrial specifications.” Customers already using the machine achieve annual outputs of up to 180,000 components in a three-shift operation.
Success at high volumes
LTH Castings in Slovenia is among the first to adopt the serial process for stator production on the RASOMA DZS 400-2. The traditional casting company has over 100 casting cells and processes raw parts on more than 250 CNC machining centres. Around 3,800 employees work across six sites. Dr Primož Ogrinec, CTO of LTH Castings, says: “With our all-in-one solutions from design to series production, we’re a key strategic partner for the automotive industry. Our range includes components for drives, motors for battery-powered electric and hybrid vehicles, steering and braking systems.” Robots load and unload the RASOMA DZS 400-2 machines in ultra-modern production.
Like most automotive suppliers, LTH Castings produces components for various vehicle models. The RASOMA DZS 400-2’s flexibility, which only requires retooling of the clamping device and tool, makes it suitable for stator housing production. “With a single system using the new process, an optimal solution, tailored to manufacturer-specific needs in both quantity and quality, was developed and brought to series production maturity,” says André Ranke. Stator housing production can be carried out for diameters up to 500mm and components up to 500mm in length.
“Every housing type we’ve seen can be manufactured on the RASOMA DZS 400-2—and we’ve seen plenty,” says Thomas Lötzsch. The project team was surprised when a major car manufacturer’s housing design required an internal component indentation. The sample component from MAPAL, specially designed for the process, didn’t present this challenge. Yet MAPAL quickly had a joint solution ready with NSH Group specialists: instead of the tried-and-tested fine boring tool, an ultra-precise actuating tool with four slides from MAPAL’s product portfolio created the desired inner contour. Machine-side, a connection designed in coordination with MAPAL was ready within days and achieved series production maturity during the ongoing order. With tightly networked development structures, both companies react quickly to newly developed contours.
New benchmark for low costs per part
The RASOMA DZS 400-2 with MAPAL tool technology has become established in series production, addressing quality issues seen on traditional turning and milling machines. Thomas Lötzsch describes cases where required shape and position tolerances were not met with reliable processes, resulting in up to 50% scrap. When quality was sufficient, cycle times were inefficient, leading to higher workpiece costs. A proven manufacturing process was missing.
As price competition is tough among automotive suppliers, RASOMA DZS 400-2 development focused on minimising unit costs from the outset. This goal was achieved through high machine availability, short cycle times, machined component quality, and production with reliable processes.